About the Liver
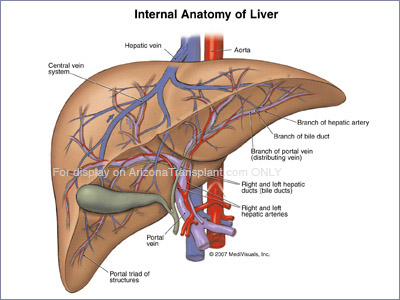
The liver is a pinkish-brown "boomerang shaped" organ in the human body. It is the second largest organ and the largest gland.
The liver plays a major role in metabolism and has a number of functions in the body including glycogen storage, plasma protein synthesis, and drug detoxification.
The liver is among the few internal human organs capable of natural regeneration of lost tissue; as little as 25 percent of remaining liver can regenerate into a whole liver again.
Volume
From 2007 - 2021, Arizona Transplant Associates have performed this volume of liver procedures.
Why is the liver important?
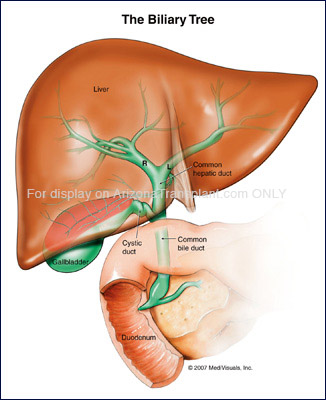
The liver is important because it stores and mobilizes energy in your body by controlling blood sugar, regulating fat storage and aiding digestion by producing bile. It also regulates blood clotting by manufacturing blood proteins and filters blood to eliminate bacteria and poisons in the system. The liver breaks down drugs, stores minerals and produces vitamins such as Vitamin D and Iron.
Liver Disease
There are several types of liver disease.
Liver diseases include:
- Hepatitis - inflammation of the liver, caused mainly by various viruses but also by some poisons, autoimmunity or hereditary conditions.
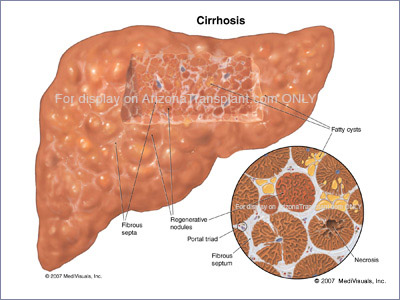
- Cirrhosis - the formation of fibrous tissue in the liver, replacing dead liver cells. The death of the liver cells can for example be caused by viral hepatitis, alcoholism or contact with other liver-toxic chemicals.
- Hemochromatosis - a hereditary disease causing the accumulation of iron in the body, eventually leading to liver damage.
- Cancer of the liver - primary hepatocellular carcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma and metastatic cancers, usually from other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Wilson's disease - a hereditary disease which causes the body to retain copper.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis - an inflammatory disease of the bile duct, autoimmune in nature.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis - autoimmune disease of small bile ducts.
- Budd-Chiari syndrome - obstruction of the hepatic vein.
- Gilbert's syndrome - a genetic disorder of bilirubin metabolism, found in about five percent of the population.
- Glycogen storage disease type II - The build-up of glycogen causes progressive muscle weakness (myopathy) throughout the body and affects various body tissues, particularly in the heart, skeletal muscles, liver and nervous system.
Treatments Provided
by Arizona Transplant Associates
Doctors Cashman, Brink, Van der Werf and Chaly offer the following liver procedures:
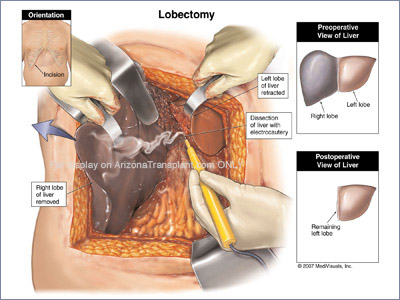
- Liver resection - Liver resection is the surgical removal of a portion of the liver. This is usually done to remove tumors that are located in the liver. The goal of liver resection is to completely remove the tumor and the appropriate surrounding liver tissue without leaving any tumor behind.
- Liver transplant - Liver transplantation is the only option for those with irreversible liver failure. Most transplants are done for chronic liver diseases leading to cirrhosis, such as chronic hepatitis C, alcoholism, autoimmune hepatitis, and many others.
Resources
American Liver Foundation, www.liverfoundation.org
Arizona Liver Disease Prevention and Liver Health Promotion, www.liveraz.org
United Network of Organ Sharing (UNOS), www.unos.org
Top Docs
chosen 20 times by their peers